Crowdin AI
Crowdin Enterprise integrates with top AI providers, including OpenAI, Google Gemini, Microsoft Azure OpenAI, and more, allowing you to leverage advanced AI-powered translations that consider additional context at different levels. These translations can be applied to your content with a few clicks using pre-translation via AI. Additionally, AI in Crowdin Enterprise can be used as an assistant in the Editor for translation, proofreading, and more.
You can expand your AI provider options by installing respective applications from the Crowdin Store.
Configuring AI
Crowdin AI integration provides powerful capabilities for enhancing localization workflows. Configuring AI involves setting up providers and creating prompts.
Configuring AI Prompts
Prompt engineering is crucial for guiding AI in understanding context and providing accurate translations. Customizing prompts within Crowdin Enterprise ensures that AI algorithms comprehend the nuances of your project, resulting in improved translation quality.
- Contextual Prompts – customize prompts to provide contextual information, such as project-specific terminology, style preferences, and target audience considerations. For example, include instructions on translating technical terms consistently or maintaining brand tone across languages.
- Placeholder Utilization – incorporate placeholders to dynamically insert context-specific information into prompts, enabling AI to generate translations aligned with project requirements.
- File-Level Context – use file-level context to provide instructions and contextual insights, enhancing AI’s understanding of content nuances. Include file descriptions, summaries, or references to glossaries and style guides.
To configure AI prompts, follow these steps:
- Open your organization’s Workspace and select AI on the left sidebar.
- In the Prompts tab, click New prompt. Alternatively, you can go ahead with creating prompt samples clicking Try a sample. Crowdin allows you to quickly set up pre-configured prompts that are ready to perform effectively from the moment they are created. While these samples are designed to work good initially, you can customize them to your personal preferences.
- In the appeared dialog, set the prompt parameters:
- Select Enabled
- Select the prompt type (i.e., Pre-translate, AI in editor, Alignment, or Create custom type)
- Custom type name (Specific to the custom type prompt)
- Title
- AI Provider
- AI Model
- Use this prompt as the default prompt for AI in editor (Specific to the AI in editor prompt type)
- Mode (i.e., Basic or Advanced)
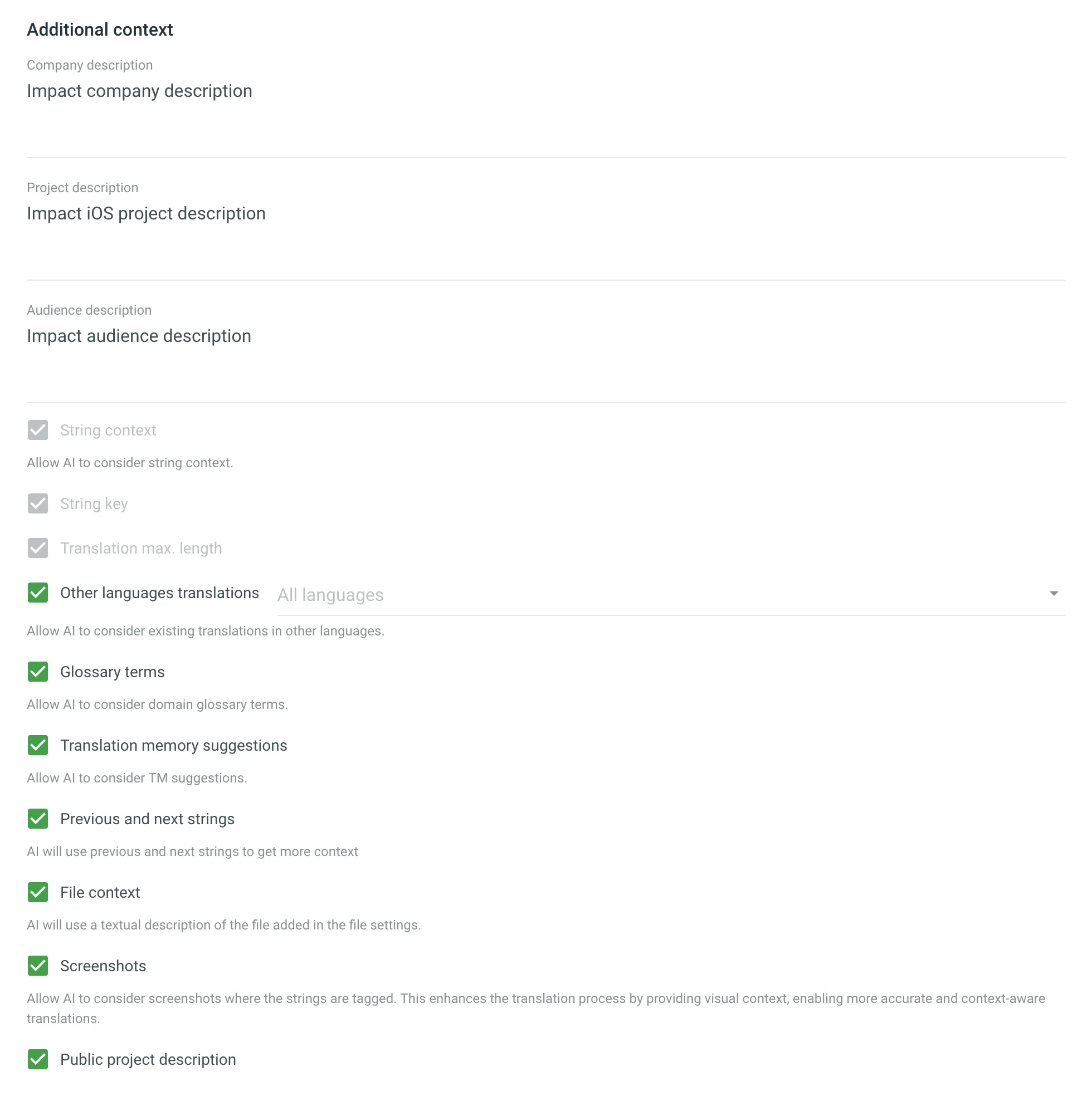
- Additional context (Basic mode) – specify which data will be included in the prompt using the following fields:
- Company description
- Project description
- Audience description
- String context
- String identifier (key)
- Translation max. length
- Other languages translations – select specific language tranlations to be considered by AI as additional context or leave this field as is to use translations from all languages.
- Glossary terms – allows AI to consider domain glossary terms.
- TM suggestions – allows AI to consider TM suggestions.
- Previous and next strings – allows AI to consider previous and next strings for additional context.
- File context – allows AI to consider a textual description of the file added in the file settings or in the Editor.
- Screenshots – allows AI to consider a visual context in the form of screenshots where the strings are tagged. This enhances accuracy and context awareness. Read more about Screenshots.
- Public project description – allows AI to consider public project description.
- Advanced mode – click Advanced mode to compose your prompt in the most precise way. While composing your prompt in the Advanced mode, you can increase translation quality by leveraging context information in your prompts using the following placeholders:
%sourceLanguage%– The name of the source language for the project.%targetLanguage%– The name of the target language for translation.%pluralForms%– A list of plural forms for the target language.%json%– A collection of strings for the current segment, including the string identifier (key), context, text, maximum length, and translations to other languages (if the translations placeholder is specified).%fileName%– The file name of the current segment.%fileContext%– The file context of the current segment (provided via the file settings modal in the ‘Files’ section).%siblingsStrings%– The previous and next segments in the file, allowing for contextual translation.%tm%– Translation Memory (TM) matches relevant to the current segment.%terms%– All the glossary terms relevant to the current segment.%projectName%– Crowdin Enterprise project name.%projectPublicDescription%– Project public description.

- Visibility – select specific projects where a prompt can be used or leave this field as is to allow a prompt usage across all projects.
- Click Create.
Managing AI Prompts
Managing AI prompts in Crowdin Enterprise involves various operations such as filtering and searching, editing, cloning, and deleting AI prompts. Below you can find instructions for each operation.
Viewing and Searching AI Prompts
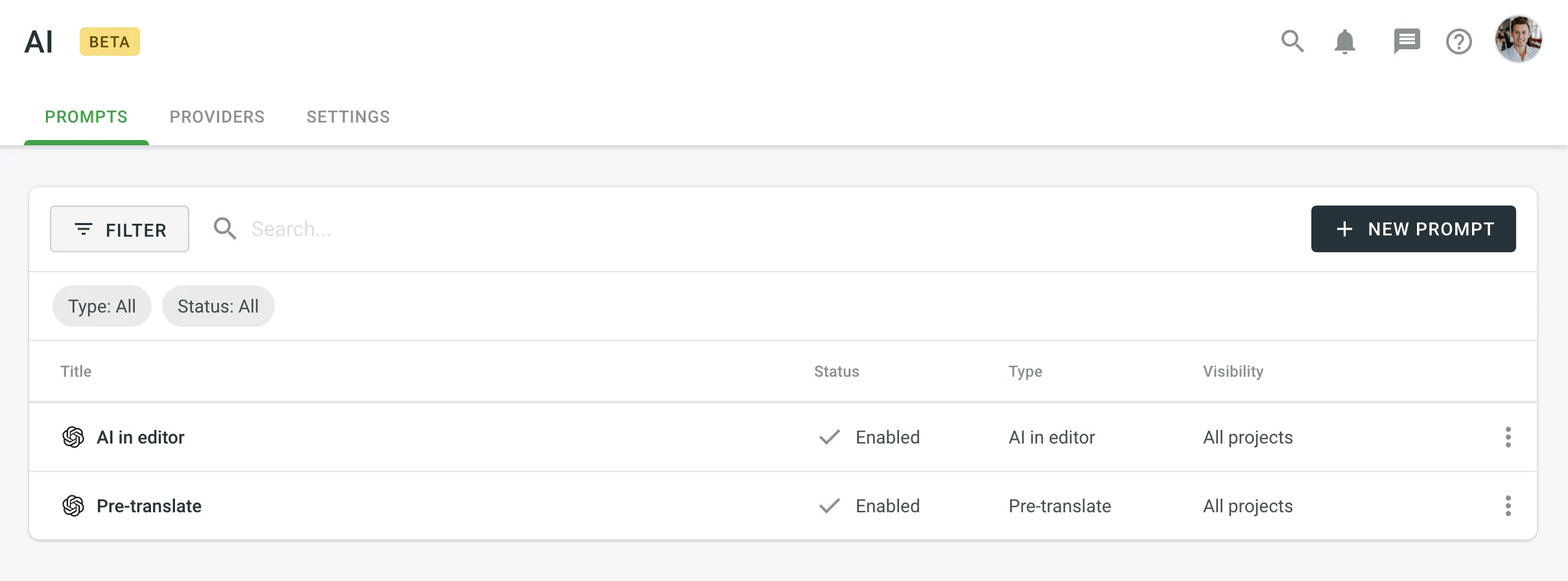
Once you open the AI page, you can view and search for prompts in the Prompts tab.
You can view the list of added prompts (one prompt per row) with the following details:
- Title
- Status
- Type
- Visibility
By default, all prompts are displayed in the Prompts tab. To filter prompts displayed, click and use the available filter options:
- Type: All, AI in editor, Pre-translate.
- Status: All, Enabled, Disabled.
To search for a particular prompt, type its title in the Search field.
Editing AI Prompts
If you need to adjust your already configured prompt, you can simply edit it.
To edit AI prompts, follow these steps:
- Open your organization’s Workspace and select AI on the left sidebar.
- In the Prompts tab, click toward the needed prompt and select Edit.
- Modify the prompt as needed and click Update to save changes.
Editing prompts allows you to update and improve them as needed to ensure they remain effective and aligned with your requirements. If you don’t want to lose the current prompt configuration and are uncertain about the changes, consider cloning your prompt and experimenting with the copy.
Cloning AI Prompts
Cloning AI prompts allows you to experiment with and refine prompt configurations without altering the original. This feature is particularly useful for testing improved versions of prompts while preserving the initial setup.
To clone AI prompts, follow these steps:
- Open your organization’s Workspace and select AI on the left sidebar.
- In the Prompts tab, click toward the needed prompt and select Clone.
- As a result, a copy of the prompt will appear in the prompt list.
You can then edit the cloned prompt to experiment with different configurations. This allows you to safely test enhancements and optimize performance without risking the loss of the original prompt configuration.
Deleting AI Prompts
Deleting AI prompts is a straightforward process, but it should be done with caution to avoid losing valuable configurations. This action is useful when you no longer need a specific prompt or want to clean up unused prompts.
To delete AI prompts, follow these steps:
- Open your organization’s Workspace and select AI on the left sidebar.
- In the Prompts tab, click toward the needed prompt and select Remove.
- Confirm the deletion.
Configuring AI Providers
Crowdin Enterprise supports various AI providers, each offering unique models and features for translation tasks. By configuring providers, you can tailor AI functionality to suit your specific localization needs. Whether using managed by Crowdin services or integrating your own API keys, Crowdin Enterprise enables seamless integration with AI services.
In the Providers tab, you can view the list of providers with the following details:
- Name
- Status: Enabled, Disabled.
- Managed by Crowdin: yes, no.
- Prompts: if there are one or more prompts configured with a particular provider, you’ll see the actual number of prompts, otherwise you’ll see the Create button that redirects to the prompt creation dialog.
Currently, Crowdin Enterprise supports the following AI providers:
- OpenAI
- Google Gemini
- Microsoft Azure OpenAI
- Mistral AI
- Anthropic
New AI providers are added regularly.
When configuring AI providers, you can choose from two possible options:
- Use your own API keys – Crowdin recommends this option if data security is a concern and for enhanced privacy and ownership. This option requires an external registration for getting API keys/credentials from AI providers.
- Use Managed by Crowdin service – simplified AI integration without the need to manage your own API keys. Allows you to leverage Crowdin’s default settings and infrastructure to access AI capabilities in a convenient way. Ideal for straightforward, quick tasks. To start using AI providers managed by Crowdin, you just need to add funds to your balance.
To configure an AI provider, follow these steps:
- Open your organization’s Workspace and select AI on the left sidebar.
- In the Providers tab, click toward the needed provider and select Edit. Alternatively, just click on the needed provider.
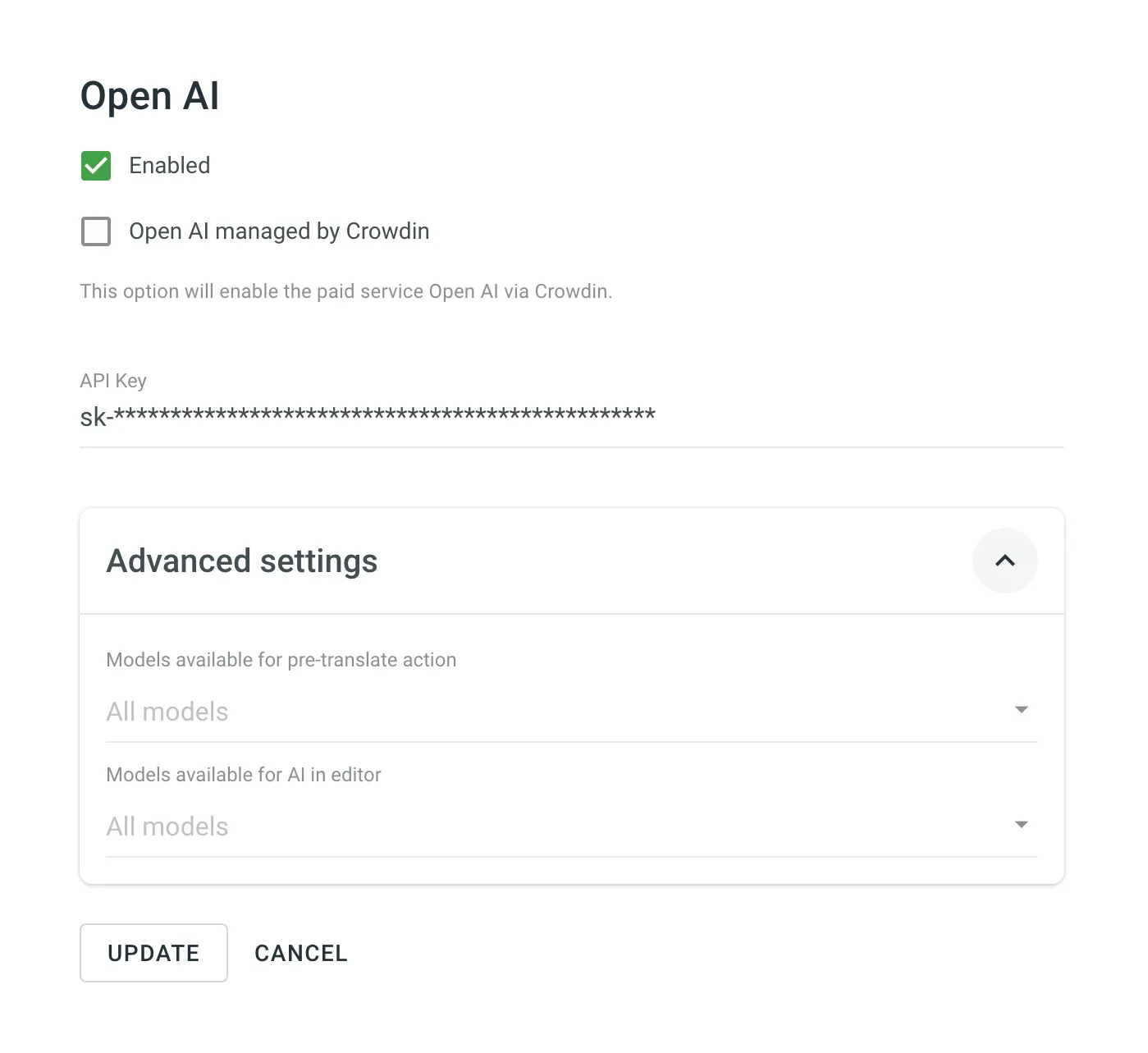
- Select Enabled.
- (Optional) Select the {Provider} managed by Crowdin option if you’d like to use the providers managed by Crowdin. In this case, you’ll need to add funds to your account balance.
- Specify your own AI provider API key. Follow AI provider instructions on how to generate an API key.
- AI providers like Google Gemini and Microsoft Azure Open AI have slightly different configuration options compared to others:
- Project ID (Specific to Google Gemini)
- Region (Specific to Google Gemini)
- Service Account Key (Specific to Google Gemini)
- Resource name (Specific to Microsoft Azure Open AI)
- Deployment name (Specific to Microsoft Azure Open AI)
- API Version (Specific to Microsoft Azure Open AI)
- Click the Advanced settings to access the model-related settings:
- In the Models section, for each prompt type (i.e., Pre-translate and Ai in editor), select the preferred models you’d like to use from the drop-down menu or leave these fields as is to use all available models.
- Click Update.
Disabling AI Providers
If needed, you can disable any of the previously enabled providers at any time.
To disable the AI provider, follow these steps:
- Open your organization’s Workspace and select AI on the left sidebar.
- In the Providers tab, click toward the needed provider and select Disable. Alternatively, click on the needed provider and clear Enabled in the provider’s settings.
Adding Funds to Account Balance
MT engines and AI models managed by Crowdin are separately paid services. To use them, you first need to add funds to your Crowdin Enterprise account balance.
Read more about Adding Funds to Account Balance.
AI Settings for the Organization
To configure default AI settings across your Crowdin Enterprise organization, open your organization’s Workspace and go to AI > Settings.
These default settings can be overridden for each project individually in the project’s Settings > AI > Settings as needed.
AI Assistant in editor
Select the default prompt for interactions with AI Assistant in the Editor across all projects in your Crowdin account.
AI Suggestion in editor
Select the default prompt for AI suggestions that will appear in the Editor across all projects in your Crowdin account. If no account-wide setting is configured and no prompt is manually selected for a specific project, AI suggestions will not be displayed in the Editor for that project. Once a prompt is selected, Crowdin will use it to generate and display translation suggestions in the Editor.
AI Alignment
When enabled, AI Alignment automatically generates bilingual draft terms based on the translations made in the project, providing additional context for both human translators and AI. This feature enhances translation accuracy and consistency without requiring additional input.
Shortcuts for chat with AI in editor
Shortcuts provide quick actions in the Editor to start AI interactions. Create shortcuts with specific instructions for the AI to quickly access frequently used actions across projects. These shortcuts are global, applying to all projects within your organization, although individual users can create their own in the Editor Settings > AI tab.
In the Shortcuts for chat with AI in editor section, you can view shortcuts with the following details:
- Name – shortcut name.
- Status – indicates whether the shortcut is enabled or disabled.
- Prompt – the prompt text associated with the shortcut.
Click on the necessary shortcut to open the context menu.
Using the available options, you can do the following:
- Edit – update the shortcut name and prompt text.
- Enable – enable the shortcut.
- Disable – disable the shortcut.
- Delete – delete the shortcut.
Use the Search field to search for specific shortcuts.
To create a new global shortcut that will be available for all projects in your organization, follow these steps:
- Click Add shortcut in the Shortcuts for chat with AI in editor section.
- In the appeared dialog, select Enabled.
- Specify a shortcut name and a prompt text it will be using.
- Click Create.
Pre-translation via AI
Pre-translation via AI allows you to use AI Models to pre-translate your content with high-quality, context-aware translations.
Using AI in the Editor
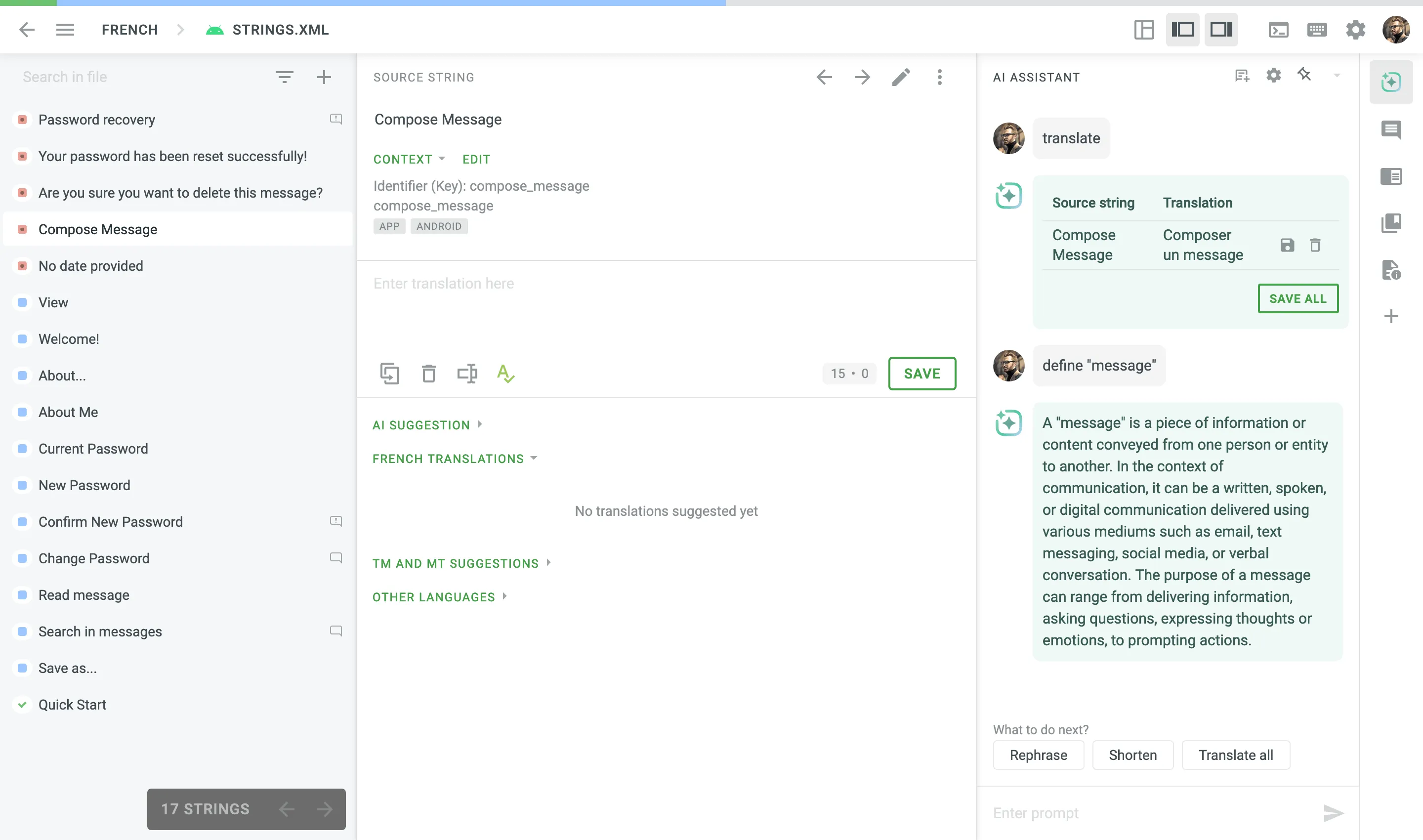
After configuring a prompt with the AI in editor type, Crowdin AI can be used in the Editor as an AI Assistant for translators and proofreaders. This AI Assistant can be communicated with in a chat format, allowing you to send prompts and receive replies.
The AI Assistant is context-aware, meaning it knows the string the translator is working on, the related glossaries, TM matches, the maximum acceptable length of the translation, the related screenshots, etc. This contextual awareness enables the AI Assistant to provide more accurate and relevant assistance.
Here are some tasks the AI Assistant can help with:
- Correcting TM suggestions: If you get a 60% match, the AI Assistant can improve the remaining 40%, ensuring consistency with your terminology and previous translations.
- Serving as an advanced dictionary: The AI Assistant can provide term definitions, translation variants, synonyms, and more.
- Suggesting translations: Similar to other MT tools, the AI Assistant can suggest translations which you can further refine based on your specific needs or save as is.
In addition, the AI Assistant can help in translating knowledge base articles by providing short summaries, helping you grasp the content quickly before translating.
When working in the Editor, you can start using the AI Assistant by clicking the AI Assistant tab in the right sidebar.
For faster and more efficient interaction with the AI Assistant, you can use prompt shortcuts. By default, there are three prompt shortcuts available:
- Rephrase
- Shorten
- Translate all
To add your own prompt shortcuts, follow these steps:
- Click in the upper-right corner to open the AI settings.
- Click Add shortcut.
- Specify a shortcut name and a prompt it will be using.
- Click Save.
Additionally, in the Editor Settings > AI tab, you can create a custom prompt to provide the AI Assistant with a specific set of instructions that are sent each time you make a request. Note that the custom prompt is project-specific.
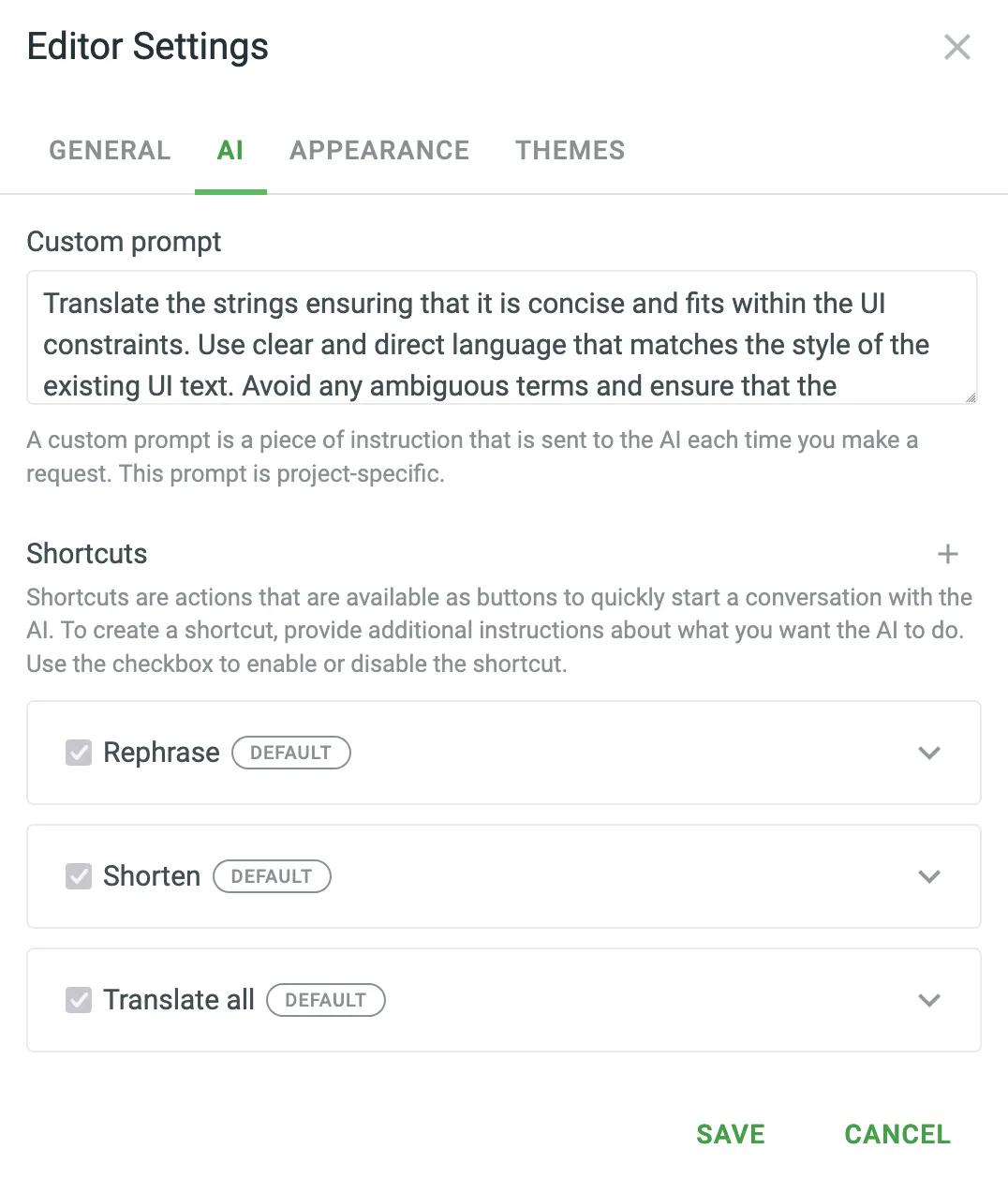
When sending prompts to the AI Assistant, the instruction priorities are considered in the following order:
- Instructions specified in the AI in editor prompt settings.
- Instructions specified in the custom prompt settings.
- Instructions specified in the prompt shortcut or manually entered in the AI Assistant chat.
AI Alignment
AI Alignment uses AI to analyze human translations, automatically generating glossary term drafts based on recurring terminology patterns. These terms add valuable context for both translators and AI, supporting consistent terminology across all project translations. Note that AI Alignment only analyzes translations submitted by users in the Editor or those uploaded to the project; pre-translations are not considered.
How AI Alignment Works
When a translator submits a translation, AI Alignment analyzes the terminology used to identify and suggest draft glossary terms. This process involves reviewing translations for recurring terms and phrases that represent core project terminology. AI Alignment then generates glossary records in simplified forms (e.g., location rather than locations) to create a unified set of terms for the project.
For example, in a project with the source string Remove this location, the initial AI suggestion for translation might be Видалити це місце. However, a human translator chooses Видалити цю локацію, using локація consistently for location. Based on this choice, AI Alignment creates a draft glossary term that pairs location with локація.
Later, when another source string Add location is translated, the AI now aligns with this glossary term and suggests Додати локацію, ensuring consistency. This will happen if the AI Prompt for AI Suggestion in editor is set to consider glossary terms.
Additionally, when human translators encounter source strings that contain location, they will see the glossary term location along with its translation локація. This helps translators use the preferred terminology, enhancing consistency across the project.
If an existing term differs from the suggested AI translation, AI Alignment will add a draft term to the current record, allowing project managers to review and confirm preferred terminology. This approach ensures new terms don’t overwrite or conflict with established glossary records.
Setting Up AI Alignment
To use AI Alignment, configure a prompt with the Alignment type and apply it to the needed projects. This prompt type enables AI Alignment to process and generate draft glossary terms as translators add their translation suggestions.
In Advanced mode, project managers can further customize specific criteria for generating glossary terms from translations. This includes filtering terms to draft only those relevant to specific domains or adjusting tolerance levels to minimize irrelevant suggestions. Such customization allows AI Alignment to focus on essential terminology for the project.
For example, managers can set AI Alignment to create term drafts only for industry-specific terminology, ensuring that only relevant records are included.
Once configured, all draft terms generated by AI Alignment appear in the glossary with a draft status, allowing managers to review and confirm these terms before they become part of the active glossary. This review step provides control over terminology consistency and accuracy across the project.